Reverse Genetics
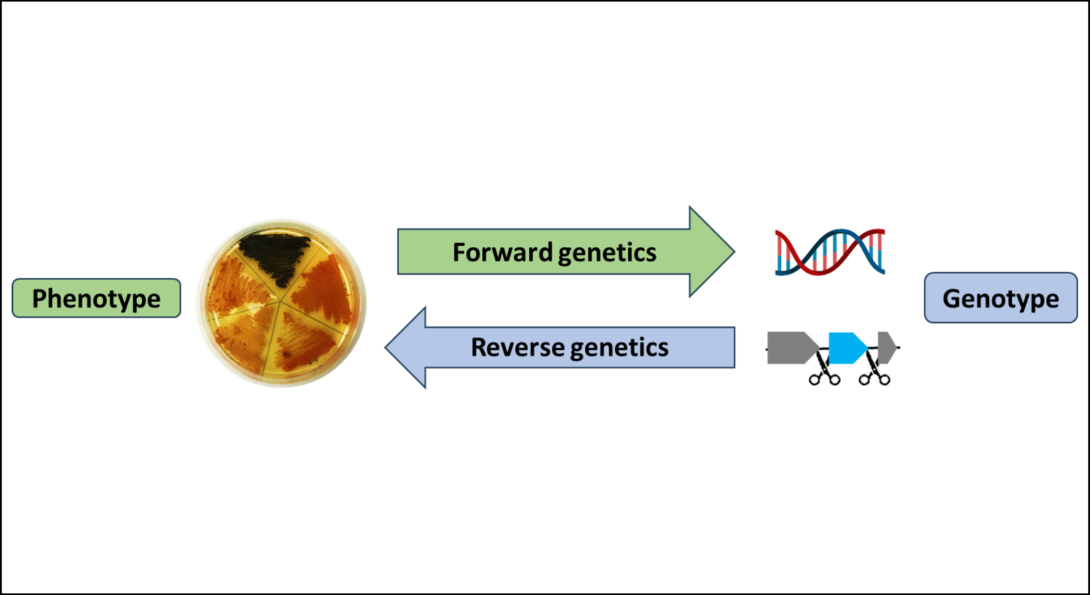
Forward and reverse genetics
Introduction
Classic, forward genetics examines the genetic cause of a phenotype (an observable characteristic such as the production of a pigment).
Now with genomes widely available, one can directly interrogate the function of a gene by creating deletion mutants for example and this is called reverse genetics.
We are interested in establishing reverse genetics tools for non-model bacteria to facilitate biosynthetic studies and to investigate the roles that natural products play in the environment (1-4).
References from our laboratory
- Dai Y, Eustáquio AS* (2025) Evaluation of vectors for gene expression in Pseudovibrio marine bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. e0020725.
- Dai Y, Lourenzon V, Ióca LP, Al-Smadi D, Arnold L, McIntire I, Berlinck RGS, Eustáquio AS* (2025) Pseudovibriamides from Pseudovibrio marine sponge bacteria promote flagellar motility via transcriptional modulation. mBio 16:e0311524.
- Ióca LP, Dai Y, Kunakom S, Diaz-Espinosa J, Krunic A, Crnkovic CM, Orjala J, Sanchez LM, Ferreira AG, Berlinck RGS, Eustáquio AS* (2021) A Family of Nonribosomal Peptides Modulate Collective Behavior in Pseudovibrio Bacteria Isolated from Marine Sponges. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 60:15891-15898.
- Braesel J, Crnkovic CM, Kunstman KJ, Green SJ, Maienschein-Cline M, Orjala J, Murphy BT, Eustáquio AS (2018) Complete Genome of Micromonospora sp. Strain B006 Reveals Biosynthetic Potential of a Lake Michigan Actinomycete. J Nat Prod 81:2057-2068.